Understanding Blood Pressure: What is Normal Blood Pressure and How to Maintain It
27 December 2023
High blood pressure is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a silent killer that often goes unnoticed until serious complications arise. Understanding what is considered normal blood pressure and how to maintain it is crucial for overall well-being. In this blog, we will explore the concept of blood pressure, its significance, the range of normal values, and practical tips to promote healthy blood pressure levels.
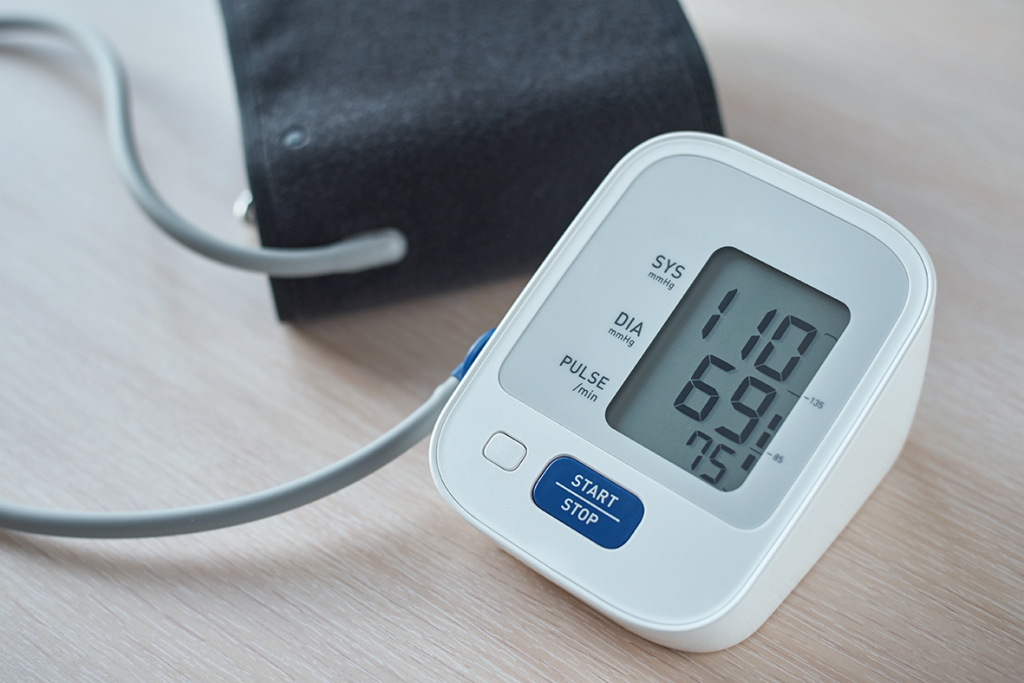

What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of the arteries. It is typically expressed as two values: systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure (the top number in a blood pressure reading) is the force when the heart contracts and pumps blood, while the diastolic pressure (the bottom number in a blood pressure reading) signifies the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
The Importance of Normal Blood Pressure
Maintaining normal blood pressure is essential for optimal health. When blood pressure is consistently high, it puts extra strain on the heart, arteries, and other organs. Over time, this strain can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision loss. On the other hand, having low blood pressure can cause dizziness, fainting, and inadequate blood flow to vital organs.
What is Normal Blood Pressure?
To determine what is considered normal blood pressure, healthcare professionals rely on established guidelines. The current standard defines normal blood pressure as a systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg. However, it’s important to note that these values may vary slightly depending on individual factors such as age, gender, and overall health.
Blood Pressure Range and Categories
Blood pressure readings can be categorised into several ranges, each indicating different levels of risk:
- Normal blood pressure: systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg. Individuals within this range have the lowest risk of developing cardiovascular problems.
- Elevated blood pressure: systolic pressure ranging from 120 to 129 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg. While not classified as high blood pressure, it serves as a warning sign and indicates the need for lifestyle modifications to prevent hypertension.
- Stage one hypertension: systolic pressure between 130 and 139 mmHg, or diastolic pressure between 80 and 89 mmHg. At this stage, intervention through lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication is typically recommended.
- Stage two hypertension: systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher, or diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher. Stage two hypertension requires immediate medical attention and a comprehensive treatment plan.
Factors Affecting Blood Pressure
Several factors can influence blood pressure readings and affect what is considered normal for each individual. Understanding these factors can provide insights into why blood pressure may fluctuate and help in maintaining healthy levels.
Age and Gender
As individuals age, their blood vessels tend to become stiffer, which can lead to higher blood pressure. Additionally, men generally have a higher risk of developing high blood pressure until around the age of 64, while women tend to have a higher risk after menopause.
Genetics and Family History
Genetics play a significant role in determining blood pressure tendencies. If you have a family history of hypertension, it’s crucial to be vigilant and proactive in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Lifestyle and Dietary Habits
Unhealthy lifestyle choices and poor dietary habits can contribute to high blood pressure. A diet high in sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol, coupled with a sedentary lifestyle, can increase the risk of developing hypertension. Incorporating a balanced diet and regular physical activity into your routine can significantly impact blood pressure levels.
Body Weight
Excess body weight, particularly when concentrated around the waistline, puts strain on the heart and increases the risk of high blood pressure. Maintaining a healthy body weight through a combination of a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential for optimal blood pressure.
Stress Levels
Stress triggers temporary increases in blood pressure, but chronic stress can contribute to long-term high blood pressure. Developing effective stress management techniques, such as practising relaxation exercises or engaging in enjoyable activities, can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Seeking Medical Advice and Treatment
While lifestyle modifications can go a long way in managing blood pressure, some individuals may require additional medical intervention. If your blood pressure consistently exceeds the normal range or if you have underlying health conditions, your healthcare provider may recommend specific medications or therapies to help regulate your blood pressure effectively.
It’s essential to maintain regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your blood pressure and discuss any concerns or questions you may have. They can provide personalised guidance based on your individual circumstances and ensure that your blood pressure remains within a healthy range.
Empowering Yourself: Lifestyle Changes for Healthy Blood Pressure
Taking control of your blood pressure involves making positive changes to your lifestyle. While medications may be necessary for some individuals, lifestyle modifications play a significant role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Here are some strategies to empower yourself in managing your blood pressure:
Adopt a Balanced Diet
Emphasise whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. Reduce your intake of processed and high-sodium foods, as excess sodium can contribute to high blood pressure.
Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Incorporate aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, into your routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to promote cardiovascular health and help regulate blood pressure.
Manage Stress
Stress can contribute to elevated blood pressure levels. Explore stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring you joy and help you relax.
Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure. If you choose to drink, do so in moderation. For women, this means no more than one drink per day, while men should aim for no more than two drinks per day.
Quit Smoking
Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of high blood pressure. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your overall health and blood pressure. Seek support from healthcare professionals, join smoking cessation programs, or explore nicotine replacement therapies to help you quit.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy body weight is essential for blood pressure management. If you are overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can have significant benefits for your blood pressure. Combine a balanced diet with regular physical activity to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Limit Sodium Intake
Reducing your sodium intake can help lower blood pressure. Avoid high-sodium processed foods and opt for fresh, whole foods instead. Be mindful of hidden sources of sodium, such as condiments, canned soups, and packaged snacks.
Increase Potassium-Rich Foods
Potassium helps counteract the effects of sodium and can help lower blood pressure. Incorporate potassium-rich foods into your diet, such as bananas, spinach, avocados, sweet potatoes, and tomatoes.
Limit Caffeine
While the effects of caffeine on blood pressure can vary from person to person, it’s generally advised to limit caffeine consumption. Monitor your body’s response to caffeine and adjust accordingly.
Get Sufficient Sleep
Inadequate sleep or poor-quality sleep can contribute to high blood pressure. Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night to support overall health and blood pressure regulation.
Monitor Your Blood Pressure
Regularly check your blood pressure at home using a home blood pressure monitor. This allows you to track your readings and identify any significant changes. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate schedule for monitoring.
Follow Medication Guidelines
If you have been prescribed medication for high blood pressure, take it as directed by your healthcare provider. Do not stop or adjust your medication without consulting them first.
Manage Chronic Conditions
Conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, and kidney disease can increase the risk of high blood pressure. Proper management of these conditions, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes, you can take an active role in managing your blood pressure and promoting overall cardiovascular health.
Complications of High Blood Pressure
When blood pressure remains consistently high, it can lead to various complications and negatively impact overall health. Understanding the potential consequences of uncontrolled hypertension highlights the importance of maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Cardiovascular Disease
High blood pressure significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure. The elevated pressure puts strain on the heart, causing it to work harder to pump blood. Over time, this can lead to the thickening and narrowing of the arteries, reducing blood flow to vital organs and increasing the risk of heart-related complications.
Stroke
Hypertension is a major risk factor for stroke, which occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted. High blood pressure weakens and damages blood vessels, making them more prone to rupturing or forming blood clots. This can result in an ischemic stroke (caused by a clot) or a hemorrhagic stroke (caused by a burst blood vessel). Both types of stroke can have severe and potentially life-threatening consequences.
Kidney Disease
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluid from the body. High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to function properly. This can lead to kidney disease or even kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Vision Loss
Uncontrolled hypertension can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems and, in severe cases, permanent vision loss. It can cause retinopathy, a condition characterised by damage to the retina, as well as other eye-related complications.
Other Health Conditions
High blood pressure increases the risk of developing other health conditions, including peripheral artery disease (reduced blood flow to the limbs), aneurysms (weakened blood vessels that can rupture), and cognitive decline (including an increased risk of dementia).
Well-Regulated Blood PressureUnderstanding blood pressure and what is considered normal is the first step in maintaining optimal health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can take control of your blood pressure and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Everyone’s blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day, influenced by various factors. Regular monitoring, healthy habits, and open communication with your healthcare provider are essential in achieving and maintaining healthy blood pressure levels. Prioritise your cardiovascular health and enjoy the benefits of a well-regulated blood pressure.
FAQ
- What should my blood pressure be?
For most adults, normal blood pressure is defined as a systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg. However, individual factors may slightly influence these values. - What is the normal blood pressure range?
The normal blood pressure range falls within the systolic pressure range of 90-120 mmHg and the diastolic pressure range of 60-80 mmHg. Blood pressure values within this range indicate a healthy cardiovascular system. - What is a good blood pressure reading?
A good blood pressure reading is considered to be within the normal range, which is a systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg. - What is normal blood pressure for adults
Normal blood pressure for adults typically falls within the range of systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalised blood pressure recommendations. - What is normal blood pressure for women?
The normal blood pressure range for women is the same as for men. It is characterised by a systolic pressure below 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg.
You may like these too
“The Hidden Dangers of Varicose Veins: When Ornate Legs Are in Danger”
Discover the unexpected causes, symptoms, and latest varicose vein treatments that can affect your h
24 January 2025
“The Inaudible Burden: How Tinnitus Can Change Your Life”
“Discover the hidden battle against the constant buzz in your ears and learn how to rega
24 January 2025
“Migraine: More than just headaches”
“Discover the hidden causes, effective treatments and tips to overcome the daily battle agains
24 January 2025
How to Lower My High Cholesterol:Tips and Advice for a Healthier Heart
Cholesterol is a common health problem that can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular
17 April 2024



